Physical series "NUCLEI, PARTICLES, FIELDS", Issue 3/59/, 2013
Drift turbulence in plasma of lower hybrid solitary structures In the Earth’s ionosphere (Rus.)
Partial Hamiltonian formalism, multi-time dynamics and singular theories (Rus.)
Neutral strange hadron production in heavy ion collisions at energies
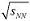 = 8,7-17,3 GeV (Rus.)
= 8,7-17,3 GeV (Rus.)J-dependence of the polarization observable of stripping reactions at low energies on lightweight nuclei (Rus.)
Analysis of synchrotron radiation emitted by runaway electrons in tokamaks
Influence of the safety factor variation on excitation of resonant magnetic perturbation in tokamak rotating edge plasmas
Waves of magnetized plasma-filled waveguide with zero value of either of two transverse wavenumbers
On opportunity of droplet sputtering of heavy metals by heavy ions of low and intermediate energies (Rus.)
Effect of the flat electrode diameter on the ignition and burning of DC discharge (Rus.)
The Child-Langmuir collisional laws for the cathode sheath of glow discharge in nitrogen (Rus.)
Photoluminescence and catalytic performance of gamma activated ZnO nanoparticles (Rus.)
The energy resolution of the X-ray spectrometer with Si(Li) detector (Rus.)
The structure and EPR of the lowsize powders KNb1-xFexO3 (Rus.)
Peculiarities of hydrogen sorbtion by metal-hidride in plasma of glow discharge (Rus.)
Materials on the basis of zirconium for creating of medical implants (Rus.)
The analysis of thermal regimes of spent nuclear fuel storage at accident conditions (Rus.)

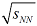 = 8,7-17,3 GEV
= 8,7-17,3 GEV