Physical series "NUCLEI, PARTICLES, FIELDS", Issue 2/50/, 2011
Title Page
 (25 kB)
(25 kB) ARTICLES
Divergences of integrals for green functions of Klein-Gordon and Dirac equations and necessary existence of particle generations (Eng.)
The nuclear gamma-resonance in research of gravitation and relativistic uniformly accelerated motion. Detecting of Mossbauer spectra of rotating objects (Rus.)
Theoretical model describing growth of single-walled carbon nanotubes in plasma (Rus.)
The fusion product losses due to resonant magnetic perturbations in toroidal plasmas (Eng.)
Photo- and electrofission of tungsten nucley in the oriented single crystal (Rus.)
Hall a Moller polarimeter (Jefferson Lab) with electron target polarized in foil plane (Rus.)
Model verification of the semiconductor gamma-ray detectors (Rus.)
Properties of superhard nanostructured coatings Ti-Hf-Si-N (Eng.)
Coexistence of various types of conductivity in Y1-xPrxBa2Cu3O7-δ single crystals with different concentrations of praseodymium (Ukr.)
The microstructure and distribution of second phase particles in austenitic steels (Rus.)
Influence of ion irradiation on the structure surface of zirconium alloys (Rus.)
Research of character of destruction and mechanical properties of hafnium in area of temperatures of 77-673K (Rus.)
Anomalous temperature dependence of surface diffusion in restricted systems (Rus.)
On the new approach to the description of phase transformations and fragility of strongly nonequilibrium systems (Rus.)
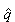 for the Klein - Gordon equation or the Dirac equation, respectively. The corresponding generalizations of the Klein - Gordon and Dirac equations have 2N and N degree, respectively. The solutions of these generalizations for the Klein - Gordon and Dirac equations may be presented by the sum of N terms, each term corresponds to the contribution of one particle (one generation). All these particles have different masses but the same spin, parity, charge, isospin. Since the space - time is 4 - dimensional one, the convergence of the integrals for proposed Green functions is possible only if the generation number N is not less than three for integer spin particles and not less than five for half - integer spin particles. It is shown that the proposed Green functions have no any singularities in the space - time. In particular, the interaction potentials must have the oscillator form at short distance. It is predicted that two (or greater) massive particles with quantum numbers of the photon and gluons must exist. Besides, five (or greater) fermions with quantum numbers of the electron, the neutrino, the quark, and quark must exist (e.g., e1=e, e2=μ, e3=τ, e4, e5,... and u1=u, u2=c, u3=t, u4, u5,...). The massless neutrino must be one. If higher neutrinos are enough heavy then the decay ν4,5 → eμν1,2 may be possible.
for the Klein - Gordon equation or the Dirac equation, respectively. The corresponding generalizations of the Klein - Gordon and Dirac equations have 2N and N degree, respectively. The solutions of these generalizations for the Klein - Gordon and Dirac equations may be presented by the sum of N terms, each term corresponds to the contribution of one particle (one generation). All these particles have different masses but the same spin, parity, charge, isospin. Since the space - time is 4 - dimensional one, the convergence of the integrals for proposed Green functions is possible only if the generation number N is not less than three for integer spin particles and not less than five for half - integer spin particles. It is shown that the proposed Green functions have no any singularities in the space - time. In particular, the interaction potentials must have the oscillator form at short distance. It is predicted that two (or greater) massive particles with quantum numbers of the photon and gluons must exist. Besides, five (or greater) fermions with quantum numbers of the electron, the neutrino, the quark, and quark must exist (e.g., e1=e, e2=μ, e3=τ, e4, e5,... and u1=u, u2=c, u3=t, u4, u5,...). The massless neutrino must be one. If higher neutrinos are enough heavy then the decay ν4,5 → eμν1,2 may be possible.